-
Definition of lubricant

Lubrication refers to the reduction of mechanical losses while making movement more harmonious by reducing frictional resistance through the supply of an appropriate substance (liquid or solid) between the frictional surfaces of 2 moving objects. Lubrication prevents damages to surfaces by separating the moving objects relative to each other by means of a membrane; the substance used in such situations is referred to as a lubricant.
Areas of application
Internal combustion engines (automobile, motorcycle, ship, train, etc.),
transmissions, industrial equipment (hydraulic equipment, compressors and turbines, etc.)LUBRICATING AREAS
-

AUTOMOTIVE ENGINE OIL
-
GREASES
-
INDUSTRIAL
-

MARINE LUBRICANTS
-
HYDRAULIC
-

THF
-

TRANSMISSION
-

POWER PLANT
-

LOCOMOTIVE
Lubricant function
-
1. Reduce friction / wear
The foremost goal of lubrication is to reduce wear in machines by reducing friction.
-
2. Cooling
Lubricants discharge the heat generated by friction and the lubrication system absorbs the heat.
-
3. Cleaning
Lubricants prevent the entry of impurities such as carbonized substances from incomplete combustion, metal fragments, or dust.
-
4. Protection of machine (anti-rust)
Lubricants protect the lubrication surface from rusting due to oxygen, moisture, or corrosive gas in the air.
-
5. Enclosure
Lubricants seal the contacting section of the machine by preventing the leakage of gas injected into the cylinder or the entry of water or dust into the cylinder.
-
6. Dispersion of forces
Lubricants uniformly disperse forces locally applied to frictional surfaces.
Accordingly, lubricants assist with the protection of equipment and extend its lifespan.
Lubricants can be thought of as similar to blood in the human body. A summary of the similarity between blood and lubricant follows.-
ACTIONS OF BLOOD
Supplies nutrients
Removes waste matter
Antibacterial
Assesses body condition
Helps to prevent abnormality in blood and blood system
-
ACTIONS OF LUBRICANT
Prevents friction and wear
Removes foreign matter
Prevents rust and corrosion
Assesses machine condition
Helps to prevent abnormality in lubricant and closure of oil channel
Lubrication
In general, the lubrication condition is divided into the following three by the thickness of the oil film of the lubricant.
-
Fluid-film Lubrication
Also known as thick film lubrication or full lubrication.
-
Boundary Lubrication

Also known as thin-film lubrication or incomplete lubrication. Or when the amount of lubricating oil is not enough, the oil film becomes thinner. Lubrication is achieved by a thin molecular film adsorbed on the friction surface.
-
Extreme Pressure Lubrication

If a heavy load is applied or the temperature of the friction surface is high, the friction surface is likely to contact and be destroyed. In order to reduce the extreme friction, the lubricant is usually added with extreme pressure additives to chemically react with the metal surface to form an extreme pressure film.
-
-
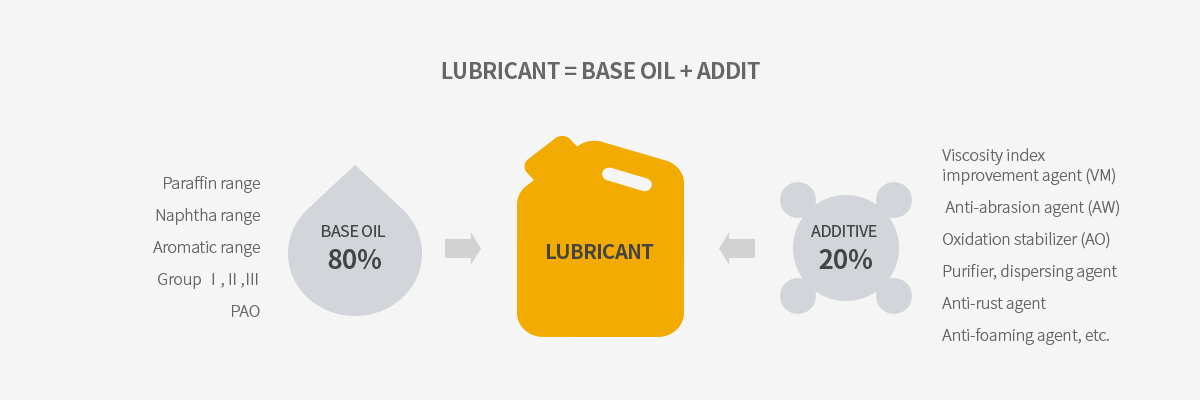
Lubricant Composition
Lubricants are largely composed of base oils and additives.
Lubricant Class
There are several middle classes of lubricants currently in use, but generally they are divided into liquid lubricants,
semisolid greases, and other solid lubricants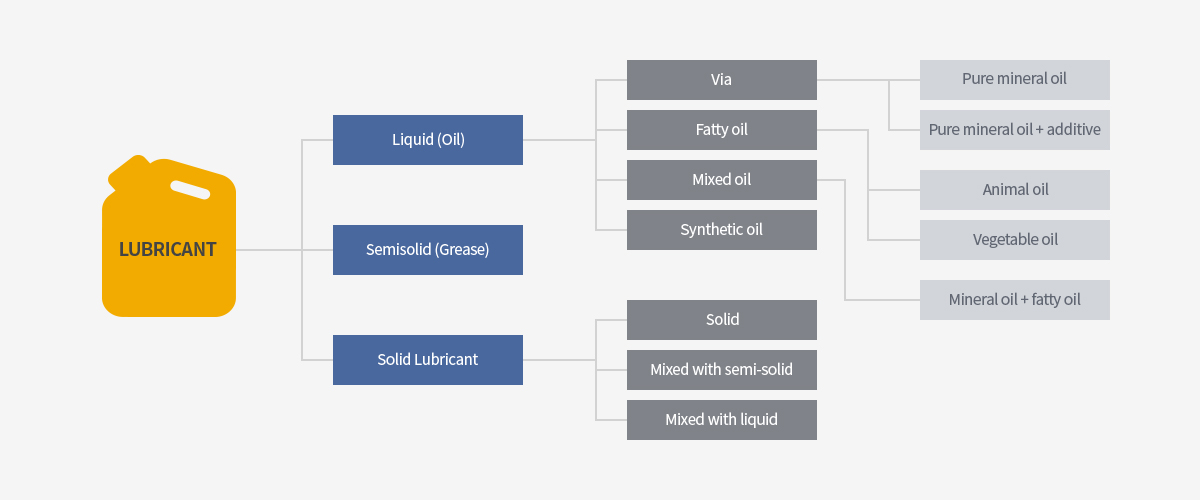
1. Mineral oil
Mineral oils manufactured from crude oil are divided into three types according to the type of crude oil.
- Paraffin Lubricant
- Naphthine Lubricant
- Mixed Lubricant
General Characteristics of Paraffinic and Naphthenic Lubricants
General Characteristics of Paraffinic and Naphthenic Lubricants Classification Paraffin Naphthine Specific gravity (S.G.) Low High Viscosity index (VI) High Low Pour point (PP) High Low Mineral oil has a Viscosity-Index representing
the change of viscosity with temperatureMineral oil has a Viscosity-Index representing the change of viscosity with temperature Kinds Viscosity inde High viscosity index (HVI) About 80 or more Midpoint Index (MVI) About 65 ~ 80 Low viscosity index (LVI) About 65 or less The oil that is used as the raw material of mineral oil-based lubricants is called base oil. Base oil is made by refining crude oil.
- Common refined oil
- Oil processed by acid, alkali, clay treatment, etc.
- Solvent-refined oil
- Oil refined using solvent, which has better oxidation stability than refined oil.
- Hydrogenated Reforming Oil
- Highly refined oil using catalyst under severe conditions of high temperature and high pressure. It has excellent performance in terms of oxidation stability compared to general refined oil.
2. Fatty oil
Vegetable oil and animal oil, used in aviation engines or in some applications for cutting, as raw materials for mixed oils and greases.
3. Mixed oil
4. Synthesized oil
Chemically synthesized lubricants from various raw materials are listed below.
- Silicone oil
- Used as precision machine oil, high temperature working oil and antifoaming agent.
- Di-Ester oil
- It is used as base oil of aircraft and jet engine, hydraulic oil and low temperature grease.
-
Lubricant classification
The classification of lubricants varies greatly depending on the criteria. Below is the classification of lubricants by engine / driveline / industrial use,
We represent our representative products belonging to the oil type.Lubricant classification Category Application Classification Remarks Our representative product Industry standard Non
Off-RoadEngine Car Gasoline (PCMO) X7 API SN Plus, ILSAC GF-5 Diesel (Gasoline),
(PCMO)No aftertreatment device Top, X9 ACEA A3/B3, A3/B4 aftertreatment device Top, X9 ACEA C1, C2, C3, C4 Bus / Truck Diesel (HDDO) No aftertreatment device X5000 API CI-4, ACEA E4 aftertreatment device X7000, 9000 API CJ-4, ACEA E6/E9 CNG ZIC CNG - Motor Cycle 2-stroke engine Fuel / Lubricant Blend (Scooter) ZIC M5 JASO FC/D, TC 4-stroke engine Engine / Transmission Simultaneous Lubrication ZIC M9, M7 JASO MA, MB Select 2-stroke engine Extra large ship SuperMar Cyl - 4-stroke engine Medium / Large Ship SuperMar TP - DriveTrain Transmission /
Differential gearAutomatic
transmission (ATF)OEM-specific transmission design
Different for each Product design requiredDEXRON VI, XP-3, ATF 6 Dexron, Mercon, etc Manual / Differential
Gear (MTF)Compared to industrial gear oil
Driving at high temperatureG-5, G-EP, G-FF MT, GL-4, GL-5 Other transmission CVT, etc CVTF Multi Shock Absorbing Oil (SAO) Mando10, Mando7 - Off-Road Industrial
Machinery /
power plant/
Construction
equipmentHydraulics
systemGeneral purpose /
low loadGeneral Purpose Hydraulic Oil SUPERVIS - For heavy loads Abrasion Resistant Hydraulic Oil SUPERVIS AW/ZF - Four seasons /
heavy equipmentHydraulic oil for heavy equipment SUPERVIS X, ZIC VEGA - turbine Steam / gas Water separation, oxidation stability,
Sludge PreventionTURBINE - Industrial gear Heavy load Operation and water separation
at low temperaturesSUPERGEAR EP - cloud bearing Grease Yield stress lubricant (Including thickener) Crown, Royal - Other Process oil (insulating oil, etc.), other than lubrication purpose (Functional Fluid) - - Like PCDO (Passenger Car Diesel Oil) or HDDO (Heavy Duty Diesel Oil, heavy truck engine oil)For diesel engine oils, there are oils available depending on whether the aftertreatment unit is installed. PCMO stands for Passenger Car Motor Oil. It refers to engine oil for passenger vehicles, especially gasoline.
Two-stroke engines in motorcycle oil are designed to produce less smoke during combustion, while four-stroke engines are designed to satisfy the friction control characteristics.In the case of ship oil, the higher the content of fuel used, the higher the infectious value is used, and in the case of small vessels, land engine oil is usually used. ATF (Automatic Transmission Fluid, Automotive Gear Oil for Automatic Transmission) is different for each car manufacturer and needs a specific product design. Hydraulic oil and turbine oil of industrial oils require water separation and oxidation stability, and gear oils require extreme pressure performance.
-
Engine oil
Viscosity specifications
Complying with SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) J300 regulations, there are low-temperature viscosity (CCS, MRV) and high-temperature viscosity (Kinematic Viscosity at 100°C, HTHS) conditions.
Viscosity specifications Viscosity rating Low temperature viscosity Kinematic viscosity (cSt) @ 100°C High temperature 26.1 shearing viscosity (HTHS, CP)
@ 1500Cranking viscosity (CSS, CP) Pumping viscosity (MRV, cP) Minimum Maximum 0W 6,200 at -35 60,000 at -40 3.8 ㅡ ㅡ 5W 6,600 at -30 60,000 at -35 3.8 ㅡ ㅡ 10W 7,000 at -25 60,000 at -30 4.1 ㅡ ㅡ 15W 7,000 at -20 60,000 at -25 5.6 ㅡ ㅡ 20W 9,500 at -15 60,000 at -20 5.6 ㅡ ㅡ 25W 13,000 at -10 60,000 at -15 9.3 ㅡ ㅡ 8 ㅡ ㅡ 4.0 6.1 1.7 12 ㅡ ㅡ 5.0 7.1 2.0 16 ㅡ ㅡ 6.1 8.2 2.3 20 ㅡ ㅡ 6.9 9.3 2.6 30 ㅡ ㅡ 9.3 12.5 2.9 40 ㅡ ㅡ 12.5 16.3 3.5(0W -40, 5W -40, 10W-40) 40 ㅡ ㅡ 12.5 16.3 13.7(15W -40, 20W 16.3-40, 40 monograde) 21.9 50 ㅡ ㅡ 16.3 21.9 3.7 60 ㅡ ㅡ 21.9 26.1 3.7 Automobile gear oil
1. Viscosity specifications
Complying with SAE J3068 for low-temperature performance (Brookfield) and high-temperature viscosity (Kinematic Viscosity at 100°C) conditions..
Viscosity specifications SAE Viscosity
GradeMaximum Temperature
for viscosity of
150,000CP°CViscosity @ 100°C
Minimum cStViscosity @ 100°C
Maximum cStApprox.
EquivalentISO
Grading0W -55 4.1 ㅡ 22-32 5W -40 4.1 ㅡ 22-46 10W -26 7.0 ㅡ 46-100 15W -12 11.0 ㅡ 100-150 20W ㅡ 7.0 <11.0 45-100 25W ㅡ 11.0 <13.5 100 8 ㅡ 13.5 <18.5 150-320 12 ㅡ 18.5 <24.5 ㅡ 16 ㅡ 24.0 <32.5 320-680 20 ㅡ 32.5 <41.0 ㅡ 30 ㅡ 41.0 ㅡ 1000 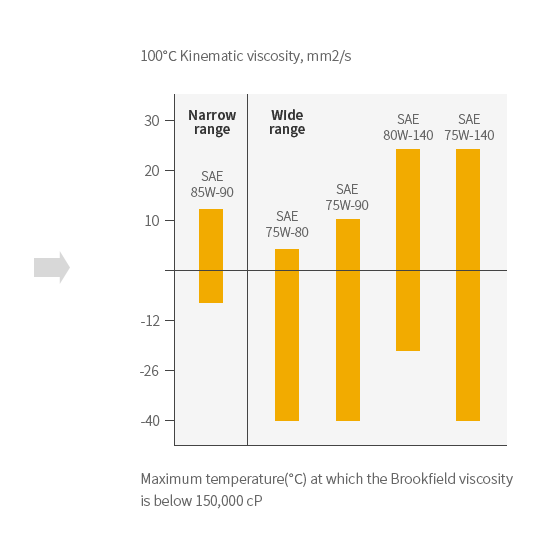
2. Performance specifications
- API772: GL-1,2,3,4,5,6, MT-1
- US Military 772 : MIL-L-2105A, 2105B, 2105C, 21050, MIL-PRF-2105ESpecifications for industrial lubricant
Viscosity specifications
Complying with ISO (International Standards Organization) regulations and classified on the basis of kinematic viscosity at 40°C.
Viscosity specifications Viscosity Grade Kinematic viscosity at 40°C [mm² /s = cSt] Mid-point Minimum Maximum ISO VG 2 2.2 1.98 2.42 ISO VG 3 3.2 1.98 2.42 ISO VG 5 4.6 4.14 5.06 ISO VG 7 6.8 6.12 7.48 ISO VG 10 10 9.0 11.0 ISO VG 15 15 13.5 16.5 ISO VG 22 22 19.8 24.2 ISO VG 32 32 28.8 35.2 ISO VG 46 46 41.4 50.6 ISO VG 68 68 61.2 74.8 ISO VG 100 100 90 110 ISO VG 150 150 135 165 ISO VG 220 220 198 242 ISO VG 320 320 288 352 ISO VG 400 460 414 506 ISO VG 680 680 612 748 ISO VG 1000 1000 900 1100 ISO VG 1500 1500 1350 1650 With industrial gear oil, the AGMA (American Gear Manufactures Association) divides this into AGMA 0-11 as follows in accordance with ISO VG (Viscosity Grade).
Viscosity specifications ISO viscosity grade Mid-point viscosity at 40°C
㎟/s1Kinematic viscosity limits at 40°C ㎟/s1 Former AGMA grade
equivalent2min max ISO VG 32 32 28.8 35.2 0 ISO VG 46 46 41.4 50.6 1 ISO VG 68 68 61.2 74.8 2 ISO VG 68 68 61.2 74.8 2 ISO VG 100 100 90.9 110 3 ISO VG 150 150 135 165 4 ISO VG 220 220 198 242 5 ISO VG 320 320 288 352 6 ISO VG 460 460 414 506 7 ISO VG 680 680 612 748 8 ISO VG 1000 1000 900 1100 8A ISO VG 1500 1500 1350 1650 9 ISO VG 2200 2200 1980 2420 10 ISO VG 3200 3200 2880 3520 11 NOTES
1The preferred unit for kinematic viscosity is mm/s, commonly referred to as centistokelcst).
2With the change from AGMA viscosity grade equivalents to ISO viscosity grade classifications, the designations S, EP, R and COMP will no longer be used as part of the viscosity grade nomenclature -
Engine oil
1. Association specifications
API (American Petroleum Institute)
: Engine oil specifications made by API and divided into gasoline and large-scale diesel. The newer the specification, the more the reinforced oxidation stability, fuel efficiency, and durability, etc.-
Gasoline
Begins with S as an abbreviation of ‘spark ignition,’ and followed by SA-SN. After using SA, SB, SC. SD, SE, SF, SG and SH, designations now being used include SJ, SL, SM, SN, SN Plus.
-
Large-scale diesel
CF4, CG-4, CH-4. CA4, C-4. CK-4(FA-4)
Begins with C as an abbreviation of ‘compression ignition,’ and is followed by CA-CK-4.
After having used CA. CB, CC. CD, CE. CF designations, CG-4, CH-4, C4, CJ-4, CK-4 have been enacted.
ILSAC (International Lubricant Standardization and Approval Committee, 2 89 standard and approval association)
: Engine oil specifications made by ILSAC composed of North American/Japanese automakers; includes GF1. 2, 3, 4 and 5. Fundamentally, they are specifications with fortified fuel efficiency performance added to API performance.
ACEA (Association des Constructeurs Europeans d'Automobilles)
: Engine oil specifications made by ACEA with emphasis on the characteristic durability and extension of the replacement interval of European vehicles compared to API or ILSAC. Generally, the specifications are amended on a 2-year interval.
Classified largely into 3 types depending on vehicle type with each type sub-classified according to performance and fuel efficiency (HTHSI/SAPS level).-
Passenger vehicle (gasoline/diesel) : A3/B3, A3/B4, A5/B5
(although there were AI/BI specifications, it was abolished at the time of the ACEA
amendment in 2016)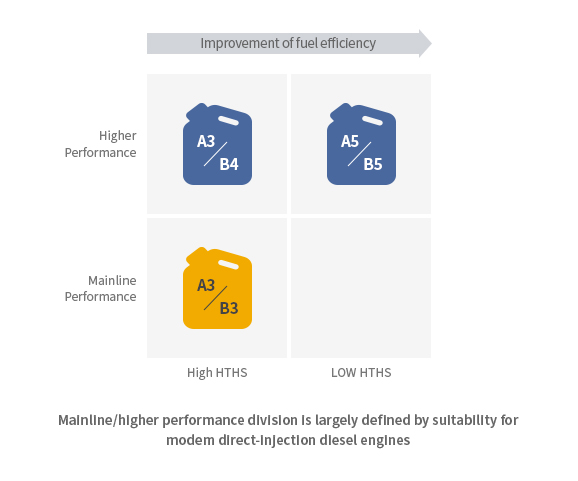
-
Large-scale diesel : E4, E6, E7, E9
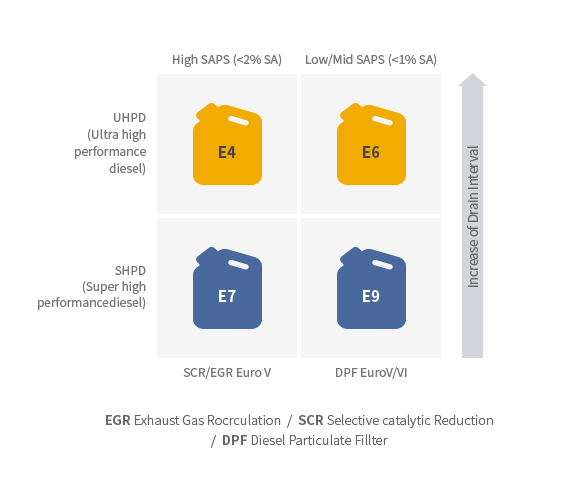
-
For vehicles with built-in, post-processing devices (emission reduction device) : C1. C2, C3. C4, C5
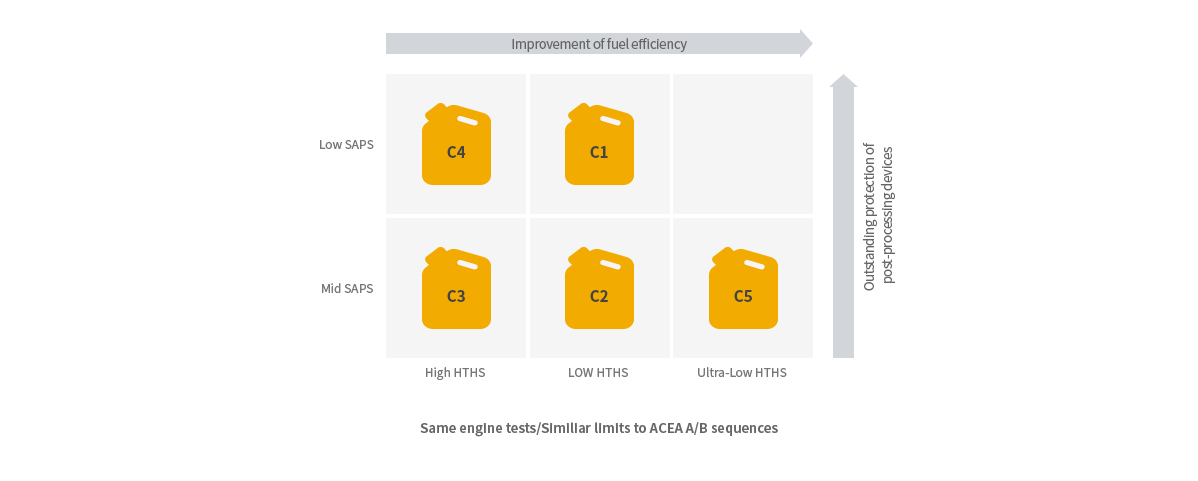
2. OEM specifications
Apart from associations (API, ILSAC, ACEA), each automaker has its own in-house oil specifications with different specifications required for each OEM. Names of the specifications of the representative OEM are as follows.
-
Passenger vehicles
Mercedes-Benz: MB 229.1, 229.3, 229.31, 229.5, 229.51, etc
Volkswagen: WW 50200, 504 00,505 00,505 01, 507 00
General Motor: Dexos 1, Dexos 2
Renault : RN 0700, 0710, 0720 -
Large-scale diesel
Mercedes-Benz: MB 228.1.228.3, 228.31.228.5.228.51, etc
MAN : M 3275, 3277,3477, etc
Volvo VDS-3, 4, 4.55, etc
Cummins : Cummins 20078, 20081, etc
Automobile gear oil
Performance specifications
API specifications : GL-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, MT-1
US Military specifications : MIL-L-2105A, 2105B, 2105C, 2105D, MIL-PRF-2105EAutomobile transmission oil
Performance specifications
Since there are many OEMs with long replacement intervals and recognized as a concept of component, there are no unified specifications per automaker as in the case of engine oil.
-
General Motor: Dexron III, VI, etc.
Ford : Mercon V, Mercon LV, Mercon SP, etc.
Hyundai : SP III, IV , etc. -
ZE: TEEML 03D, 04D, 05L, 09, 11B, 16L, 170, 14A, etc.
Chrysler : MS-1872, 5931, 9602, 10838, etc.
Specifications for industrial lubricant
Performance specifications
Oil types that belong to industrial oil are highly diversified and, as such, there are highly diversified performance specifications according to each oil type. Representative performance specifications of hydraulic oil, gear oil, and turbine oil are as follows:
-
Hydraulic oil
Denison : HF-0, 1, 2
DIN 51524 : Part I, Part II, Part III
ISO 11158 : HH, HL, HM, HV
Cincinnati Machine(CM) : P-68, 69, 70
Vickers : 104C, 35VQ25, 1-286-S, M-2950-S
Us Steel : 127, 136 -
Gear oil
AGMA 9005 : E02, F17
DIN 51517: Part I, Part II, Part III
ISO 12925-1 : CKB, CKC, CKD, CKE, CKS
US Steel : 224 -
Turbine oil
DIN 51515 : Part I, Part II
General Electric: GEK-32568, GEK-107395
-
-
Trends in lubricants

-
 Improvement of fuel efficiency
Improvement of fuel efficiencyStriving to improve fuel efficiency by lowering viscosity and friction, as well as improving performance of oil in order to cope with the fuel efficiency regulations of each country.
-
 Long Drain Interval
Long Drain IntervalStriving for long drain intervals (replacement intervals) by fortifying the durability of the oil through performance improvement of volatility and oxidation stability of base oil and additives.
-
 Compatibility with post-
Compatibility with post-
processing deviceReducing SAPS (Sulfated Ash, Phosphorous, Sulfur) contents in oil for the protection of performance and lifespan extension of post-processing devices (SGR, EGR, and DPF, etc.) introduced to cope with gas emission regulations.
-